Niger

niger, AN OVERVIEW
Niger has 22.3 million inhabitants and a high rate of population growth (with a fertility rate of 7.1 children per woman); its economy is poorly diversified and primarily dependent on agriculture, which accounts for 40% of its gross domestic product (GDP).
Despite the significant progress made by Niger in the past decade to reduce its poverty rate, the level of extreme poverty remains very high at 41.4% in 2019, affecting more than 9.5 million people, mainly women and children.
For several years, Niger has been grappling with a significant influx of refugees fleeing conflicts in the region, particularly in Nigeria and Mali (221,671 refugees and 196,717 displaced persons according to the HCR in April 2019).
NIGER IN FIGURES
- Total population * : 22.3 M
- Very young* population :
- 32% aged between 10 and 24
- 50% aged under 15
-
Population residing outside cities* : 83%
- Population growth rate* :
- 3,8% per year in Niger
- 1,1% per year in global terms
-
Fertility rate of women aged 15-49 (2015-2020)* : 7,1 children per woman
-
Contraceptive prevalence rate of women aged 15 to 49 (2018)* :
- 20% all methods
- 18% modern methods
- Maternal mortality ratio (2017)** : 509 deaths per 100,000 live births
- Rate of early marriage* : 63% of adolescents aged 15 to 19 married
- Early pregnancies : 74,7% of adolescents under the age of 19 pregnant or have given birth
- Unmet family planning needs* : 19% of women aged 15 to 49

Niger
THE FRENCH MUSKOKA FUND IN niger
Read about some of our high-impact interventions:
Improving the quality of care for mothers and newborns
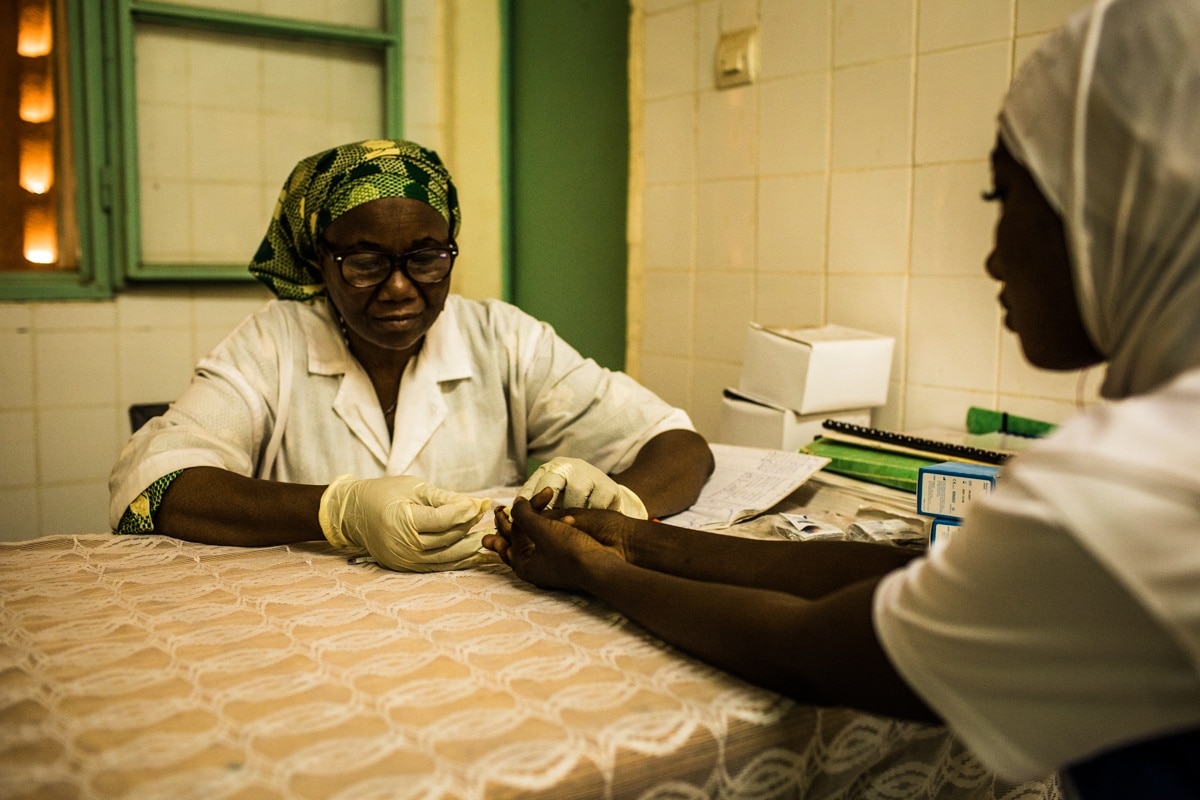
In Niger, Muskoka partner agencies have launched an initiative to improve the capabilities of service providers in 3 Mother and Child Health Centers and 44 BEmONC facilities in the Maradi, Zinder and Diffa regions. An advocacy campaign was carried out to create neonatal units in regional hospitals and assign at least one pediatrician to each unit.
Funding was provided for training and equipment in the first three neonatal units in these three regions. Since they were opened, these units have recorded an increase in newborn care (+5,262) and hospitalizations (+40,104, including 709 premature and low-birth-weight babies). Of these, 210 were cared for using the kangaroo method. The neonatal intensive care unit at the IKG maternity hospital in Niamey has also received substantial support.
The French Muskoka Fund as a leveraging tool and instrument of influence
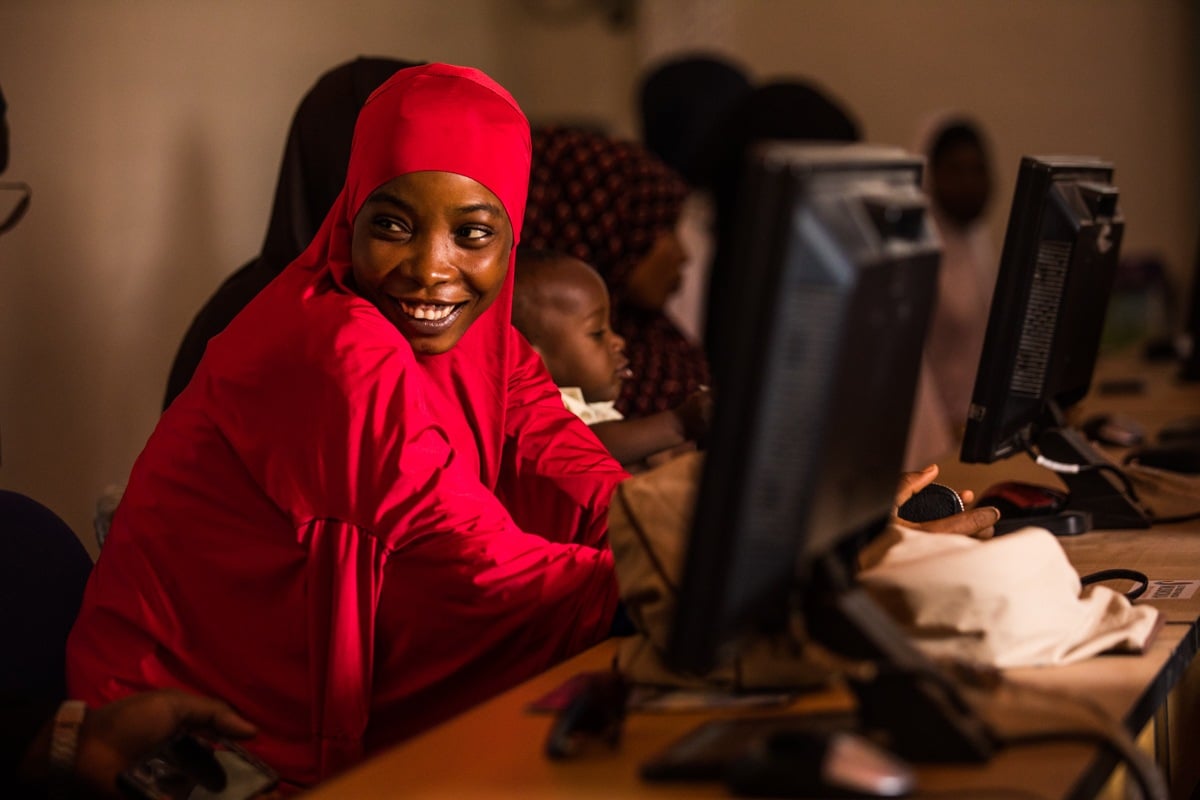

This led to a US$51 million funding package over 5 years. This funding is currently being used to implement the same high-impact interventions as those supported by the French Muskoka Fund and extend them to even more districts.
By way of an example, community-based newborn follow-up has been extended from 6 to 18 health districts.
Family planning
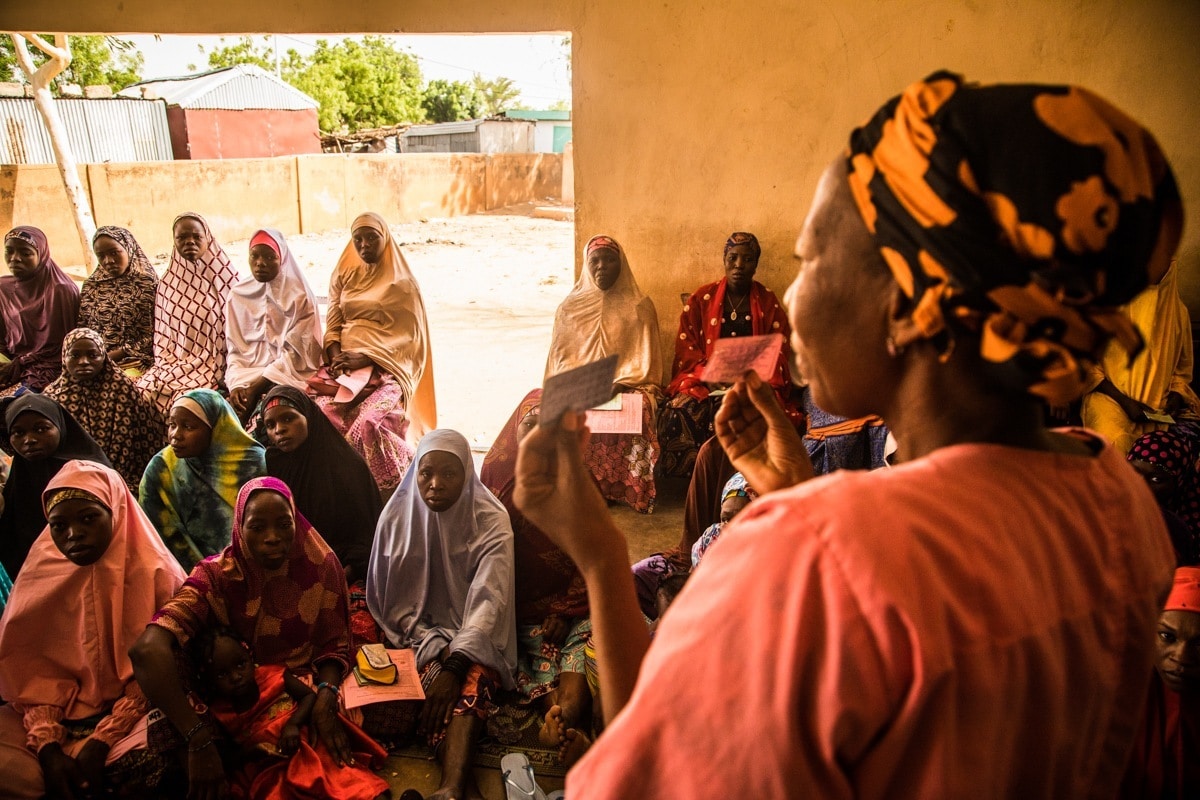

Community-based distribution of family planning products consists of ensuring family planning services are provided by community health workers, to bring these services to households that are remote from health facilities.
This has been introduced in Niger, where delegating tasks to community health workers has been made part of its health policy.
The community health workers have received training with the support of the French Muskoka Fund.
A major innovation was the addition of injectable contraceptives to the available product range.
Maternal and child nutrition
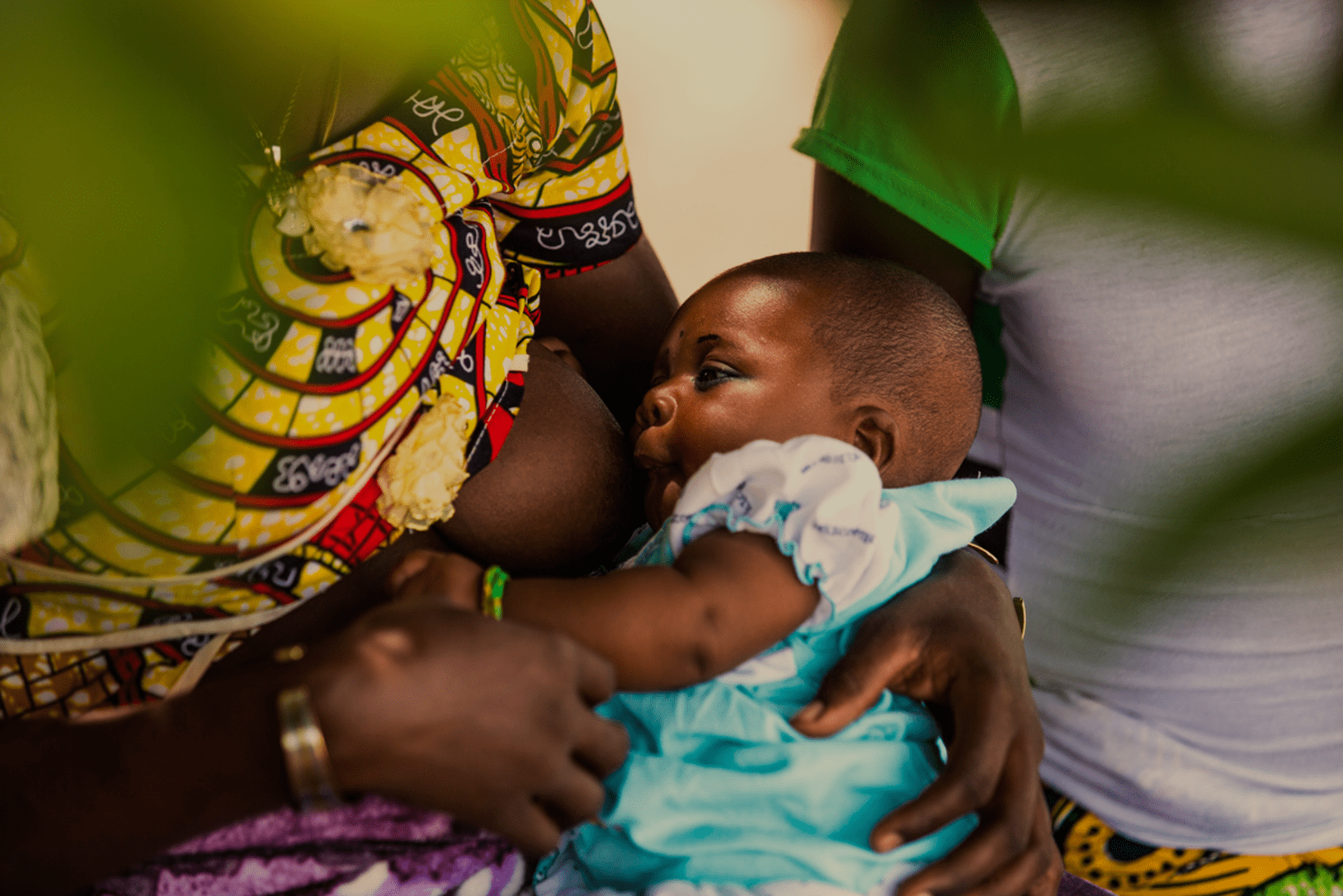
In Niger, efforts have been made since 2014 to strengthen interventions that promote, protect and support the feeding of infants and young children.
These interventions, primarily targeted at integrated health centers, rural clinics and communities, currently cover 30 health districts out of 72, i.e. 42%. The French Muskoka Fund’s contribution has helped improve two aspects of promoting and supporting infant and young child feeding: the implementation of 10 conditions for successful breastfeeding by giving fresh impetus to the “baby-friendly hospital” initiative; and the implementation of infant and young child feeding services in the Guidan Roumdji health district (Maradi region) at integrated health centers and in the community.
KEY RESULTS
MDG 4 on child mortality has been achieved by Niger.
%
reduction in newborn mortality between 1990 and 2018 in Niger
%
reduction in under-five mortality between 1990 and 2018 in Niger
%
an increase in the rate of births attended by qualified staff between 2010 and 2017 in Niger
%
growth in the number of midwives between 2012-2016 in Niger
%
rate of modern contraception use in 2018 in Niger
%
an increase in exclusive breastfeeding rates in babies under 6 months in Niger
Stories
Zouley
Maradi, Niger
Mamane
Maradi, Niger
Hamidou
Niger
Contact us
To contact us, complete the form below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
